Blockchain Quality Engineer Career Path (QA → Web3 Security & Testing Roles in 2025)

Many QA engineers and testers exploring blockchain careers run into the same problem: job listings sound security-heavy, interview expectations feel unclear, and it’s hard to tell whether companies want testers, auditors, or full-stack developers in disguise.
Blockchain quality engineering sits at the intersection of testing, security, and distributed systems — but it’s rarely explained in practical terms. Candidates often ask whether their existing QA experience is relevant, how much coding is actually expected, and what hiring teams really assess during interviews.
This guide breaks down the blockchain quality engineer career path from a QA and testing perspective. It explains what the role involves in real projects, how responsibilities evolve toward security and audit work, what skills matter at different levels, and how professionals transition from traditional QA into Web3 testing and security roles in 2025.
Who this guide is for
• QA engineers and testers exploring blockchain or Web3 roles
• Professionals confused by blockchain QA vs security vs audit expectations
• Candidates preparing for blockchain testing or security interviews
• Testers considering a long-term transition into Web3 quality or security roles
TL;DR — Blockchain Quality Engineering in 2025
• Blockchain QA is no longer just testing features; it focuses on validating assumptions, risk, and system behavior.
• Most professionals enter from traditional QA or testing roles and gradually move toward security-aware responsibilities.
• Hiring teams value judgment, failure reasoning, and communication more than tool lists or certifications.
• Salaries vary widely based on responsibility and proximity to security-critical systems, not just titles.
• Certifications help with fundamentals but rarely determine hiring outcomes without real reasoning depth.
• The strongest long-term path blends QA discipline with security awareness and system-level thinking.
What Does a Blockchain Quality Engineer Actually Do?

A blockchain quality engineer focuses on validating the safety, reliability, and correctness of blockchain-based systems — but the role is very different from traditional application testing.
Unlike conventional QA, blockchain quality engineering deals with immutable code, financial risk, and adversarial environments. A missed edge case is not just a bug; it can lead to irreversible fund loss, protocol failure, or governance exploits.
In practice, blockchain quality engineers work across three overlapping areas: smart contract testing, security validation, and system-level behavior under real network conditions. This often means testing assumptions rather than just functionality.
For example, contracts that behave correctly on local testnets may fail under mainnet conditions due to gas constraints, ordering effects, or unexpected external calls. These gaps are a recurring concern for engineers transitioning into blockchain QA.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/when-blockchain-qa-tests-pass-locally-but-fail-on-mainnet-whats
Core Responsibilities of a Blockchain Quality Engineer
Smart contract testing is a foundational responsibility, but it extends beyond validating expected outputs. Quality engineers examine how contracts behave under failure conditions, malicious inputs, and upgrade scenarios. This includes identifying risks such as reentrancy, access-control flaws, incorrect assumptions about external integrations, and unsafe upgrade paths.
As engineers gain experience, their focus shifts toward security-oriented testing. This involves validating threat models, reviewing protocol logic, and understanding how attackers might exploit economic or technical weaknesses — even when code appears correct.
Another critical responsibility is testing system behavior across environments. Blockchain applications interact with wallets, oracles, bridges, and layer-2 systems. Quality engineers validate these integrations, ensuring that assumptions hold when multiple components interact under real network conditions.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/smart-contract-qa-testing-hub
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/smart-contract-security-audits-hub
Why Blockchain Quality Engineering Became a Dedicated Role
Many high-profile blockchain failures did not happen because teams lacked developers — they happened because critical assumptions were never tested.
Bridge exploits, faulty upgrade mechanisms, and governance loopholes often pass standard test cases but fail under adversarial conditions. As protocols grew in value and complexity, teams realized that traditional QA approaches were insufficient.
This is why blockchain quality engineering evolved into a distinct role. Hiring teams now look for professionals who can reason about risk, not just write test scripts. In interviews, candidates are often assessed on how they think through failure scenarios rather than how many tools they have used.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/proof-based-hiring-in-web3
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/web3-hiring-signals
Understanding this shift is critical before evaluating salaries, certifications, or tools — because expectations differ significantly from traditional QA roles.
Career Path: From QA Engineer to Blockchain Security & Audit Roles
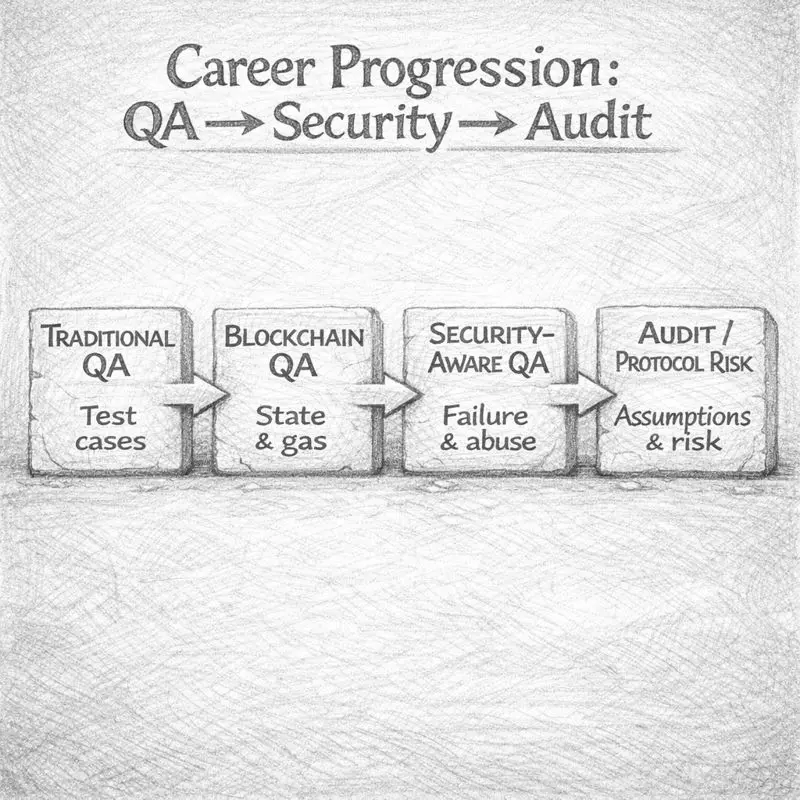
Blockchain quality engineering does not follow a single, linear career path. Most professionals enter from adjacent roles — traditional QA, test automation, backend engineering, or smart contract development — and gradually specialize based on how deeply they move into security, protocol logic, or system-level risk.
What differentiates successful transitions is not how quickly someone learns blockchain tools, but how well they adapt their testing mindset to adversarial, high-stakes environments. As responsibility increases, the role shifts from validating functionality to evaluating assumptions and failure scenarios.
=> Entry-Level: Blockchain QA Engineer
At the entry level, blockchain QA engineers focus on understanding how decentralized systems behave and where traditional testing assumptions break down.
Typical responsibilities include testing smart contract functionality on testnets, validating transaction flows, identifying edge cases related to gas usage or state changes, and collaborating closely with developers to reproduce issues. Many professionals at this stage come from traditional QA or automation backgrounds and are still building confidence with blockchain concepts.
Hiring teams usually assess candidates on clarity of thought rather than depth of protocol knowledge. Interview questions often revolve around how candidates reason through failures, explain test cases, and communicate risks rather than how many tools they know.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/moving-from-software-testing-to-blockchain-qa-need-advice
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/should-i-switch-to-blockchain-career
=> Mid-Level: Automation, Security Testing & Deeper Ownership
At the mid level, blockchain quality engineers begin taking ownership of testing strategy rather than individual test cases. This stage often marks the transition from functional testing into security-aware validation.
Engineers at this level design automated test suites, validate upgrade mechanisms, test oracle dependencies, and reason about how contracts behave under malicious or unexpected conditions. They are expected to understand common vulnerability classes and recognize when business logic, not just code, introduces risk.
Interviews at this stage increasingly resemble security or protocol discussions. Candidates are evaluated on trade-off analysis, debugging approach, and how they communicate uncertainty when systems behave unexpectedly.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/from-qa-engineer-to-blockchain-security-auditor-which-skills-help-most
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/web3-interview-signals-calibration
=>Senior-Level: Test Architect, Security Specialist, or Auditor Track
Senior blockchain quality engineers operate closer to security, architecture, and protocol design than traditional QA. Their role centers on evaluating systemic risk rather than individual defects.
Responsibilities include designing end-to-end testing strategies, reviewing protocol changes, validating governance and upgrade paths, mentoring junior engineers, and collaborating with auditors or internal security teams. Many professionals at this stage choose to specialize further into security auditing, protocol testing, or cross-chain risk assessment.
Hiring decisions for senior roles rely heavily on proof of judgment. Teams look for candidates who can explain past failures, justify trade-offs, and demonstrate how their testing decisions prevented or mitigated real-world risk.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/smart-contract-security-audits-hub
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/proof-based-hiring-in-web3
Common Specialization Paths in Blockchain Quality Engineering
As blockchain systems mature, quality engineers often specialize based on protocol complexity and risk exposure.
Some move into security auditing, focusing on vulnerability discovery, threat modeling, and audit collaboration. Others specialize in DeFi and protocol testing, validating economic logic, oracle assumptions, and governance mechanisms. A smaller subset focuses on cross-chain and interoperability testing, where failures often occur at system boundaries rather than within individual contracts.
Choosing a specialization early is less important than building strong reasoning skills and exposure to real incidents.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/smart-contract-security-news-best-sources-experts-to-follow-for-real-time
Understanding where you sit on this progression helps contextualize salary expectations, required skills, and what hiring teams evaluate at each stage.
How Blockchain Quality Engineers Are Paid (And Why Salaries Vary So Widely)
Blockchain quality engineering salaries often confuse candidates because compensation is not determined by title alone. Unlike traditional QA roles, pay in Web3 is closely tied to risk exposure, decision-making responsibility, and proximity to security-critical systems.
Two engineers with the same “QA” title may earn vastly different compensation depending on whether they are validating UI flows, testing smart contract logic, or evaluating protocol-level failure scenarios. Hiring teams price responsibility, not just experience.
At a high level, blockchain quality engineering roles typically fall into three broad compensation bands:
Entry-level and early-transition roles tend to align with mid-level software QA compensation, especially when responsibilities focus on functional testing and test automation. These roles are often used by companies to evaluate a candidate’s ability to reason about blockchain systems before increasing scope.
Mid-level roles that involve security-aware testing, upgrade validation, and protocol interaction generally command higher pay. Engineers at this stage are expected to identify systemic risk, not just surface defects.
Senior and security-focused roles — including test architects and audit-adjacent positions — are compensated at a premium. These roles are often priced similarly to security engineers or protocol specialists because mistakes directly translate into financial or reputational loss.
Geography still matters, but less than in traditional software roles. Many blockchain companies hire globally, yet compensate based on role criticality rather than location alone.
Remote-first teams tend to pay higher for security-sensitive QA roles, while regionally anchored companies may align compensation closer to local benchmarks. Candidates often misjudge offers by comparing them to developer salaries without accounting for the nature of responsibility involved.
Blockchain QA Salary in 2025: What Changes as You Move Closer to Security

Across Web3 hiring discussions, compensation increases are consistently tied to a few signals rather than years of experience.
Engineers who can explain why a failure happened, how it could have been prevented, and what trade-offs were involved tend to negotiate stronger offers. The ability to reason about incidents, upgrades, and security assumptions carries more weight than tool familiarity.
This is why many candidates with certifications or tooling exposure still struggle to justify higher compensation — while others with fewer credentials but stronger judgment move faster.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/proof-based-hiring-in-web3
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/web3-hiring-signals
Another common challenge is discussing compensation in interviews. Blockchain QA roles often span multiple responsibilities, making it difficult for candidates to anchor expectations.
Rather than quoting market averages, strong candidates frame salary discussions around scope: what systems they will own, what risks they will manage, and how their work reduces downstream failures. This approach aligns better with how Web3 teams evaluate value.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/how-to-answer-the-what-are-your-salary-expectations-question-as-a
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/salary-tokens-compensation-hub
This is why understanding skills, specialization, and expectations matters more than chasing salary numbers in isolation.
How to Switch from QA to Blockchain Security Testing (Without Becoming a Full Developer)
Blockchain quality engineering demand spans multiple sectors, but the responsibilities differ based on risk, regulation, and system complexity.
=>DeFi Protocols and Crypto-Native Companies
DeFi and crypto-native teams hire quality engineers to validate smart contract logic, protocol upgrades, oracle dependencies, and integration behavior under real network conditions. These roles often overlap with security teams because assets are directly exposed.
=> Exchanges, Wallets, and Infrastructure Providers
Exchanges, wallet providers, node infrastructure companies, and middleware platforms hire QA engineers to test transaction flows, signing behavior, failure handling, monitoring, and multi-network compatibility. Reliability and incident readiness matter as much as test coverage.
=> Enterprise and Regulated Implementations
Enterprise and regulated deployments often focus on permissioning models, audit trails, access control, privacy constraints, and compliance readiness. Here, quality engineering overlaps with process design and governance validation.
=> Gaming, NFTs, and Consumer Apps
Consumer blockchain products hire QA engineers to validate marketplace workflows, asset ownership handling, metadata integrity, and abuse scenarios — including cases where “users behave like attackers.”
If you’re evaluating which sector fits you, ask one question: will your work mostly validate features, or validate assumptions and risk?
Certifications in Blockchain QA: When They Help — and When They Don’t

Certifications are one of the most misunderstood parts of the blockchain quality engineering career path. Many candidates pursue multiple courses hoping they will compensate for lack of experience, only to discover that certifications rarely determine hiring outcomes on their own.
In Web3, certifications function as context — not proof. They can signal exposure to concepts such as smart contract security, protocol architecture, or blockchain fundamentals, but they do not demonstrate how a candidate thinks when systems fail or assumptions break.
Where Certifications Can Help
Certifications tend to be useful at early or transitional stages, especially for professionals moving from traditional QA or testing roles into blockchain environments. They help structure learning, introduce domain vocabulary, and reduce onboarding friction during interviews.
For candidates without prior blockchain exposure, certifications can support conversations by showing intentional upskilling. They are most effective when paired with hands-on experimentation, testnet work, or clear explanations of what was learned — not just what was completed.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/what-certifications-or-degrees-are-best-for-building-a-career-in-blockchain
Why Certifications Alone Don’t Unlock Senior Roles
As roles move closer to security, protocol logic, or audit-adjacent responsibilities, certifications lose influence quickly. Hiring teams do not rely on course completion to assess risk ownership, judgment, or decision-making under uncertainty.
Candidates are often evaluated on how they reason through vulnerabilities, explain failure scenarios, or justify trade-offs — areas that certifications rarely test. This is why professionals with multiple credentials sometimes struggle in interviews, while others with fewer formal qualifications progress faster.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/proof-based-hiring-in-web3
Are Blockchain QA Certifications Worth It? How Hiring Teams Read Them
During interviews, certifications are typically treated as conversation starters rather than decision factors. Interviewers may ask candidates to explain concepts referenced in their certifications or to apply them to hypothetical scenarios.
What matters is not whether a certificate exists, but whether the candidate can translate that knowledge into reasoning. Shallow answers or memorized explanations often hurt credibility more than having no certification at all.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/web3-interview-signals-calibration
Using Certifications Without Falling Into the Checkbox Trap
The most effective way to use certifications is as a foundation, not a destination. Candidates who combine structured learning with practical testing, security analysis, or incident breakdowns demonstrate far stronger signals to hiring teams.
Explaining how a concept from a course influenced a testing decision or helped identify a flaw is far more persuasive than listing credentials. This approach aligns more closely with how Web3 teams assess readiness and long-term potential.
https://artofblockchain.club/article/proof-based-hiring-in-web3-2025-how-founders-evaluate-github-tests-smart-contracts
This distinction becomes even clearer when evaluating skills and tools — where expectations often differ sharply from what most learning paths emphasize.
Skills & Tools in Blockchain QA: What Hiring Teams Actually Expect
Blockchain quality engineering is often misunderstood as a tooling-heavy role. In reality, hiring teams care far less about how many frameworks a candidate has touched and far more about how they reason about system behavior, failure modes, and security risk.
Tools change quickly. Expectations do not.
Strong blockchain QA engineers are evaluated on whether they understand why systems fail, not just how to run tests. This is especially true in interviews, where candidates are often asked to explain scenarios rather than demonstrate tool proficiency.
Foundational Skills Hiring Teams Look For
At the foundation, blockchain quality engineers are expected to understand how decentralized systems differ from traditional applications. This includes reasoning about immutability, transaction ordering, gas constraints, external calls, and the consequences of failure in financial systems.
Candidates who can clearly explain how state changes occur, how assumptions break under load or adversarial conditions, and why certain bugs are more dangerous than others consistently perform better than those who rely on memorized patterns.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/what-are-some-common-mistakes-to-avoid-in-a-blockchain-career
Security-Aware Thinking Over Tool Memorization
As roles progress, security awareness becomes a defining skill. This does not mean every QA engineer must be a full auditor, but they are expected to recognize common vulnerability classes and understand how business logic, not just code, introduces risk.
Hiring teams often probe how candidates think about access control, upgrade paths, oracle dependencies, and external integrations. The ability to walk through a hypothetical failure and explain its impact is valued far more than listing security tools.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/silent-fails-in-smart-contract-access-control-what-teams-miss-until-its-too
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/can-smart-contracts-be-audited-what-are-the-common-tools-for-auditing
How Tools Are Actually Used in Practice
Testing and analysis tools are enablers, not differentiators. Frameworks such as Hardhat, Foundry, or Truffle help execute tests, while security tools assist in surfacing known vulnerability patterns. However, tools only reveal issues when the engineer knows what to look for.
In interviews, candidates are rarely rewarded for naming tools. Instead, they are asked how they used a tool to uncover a specific issue, what assumptions guided their testing, and what they would do differently if a test passed but risk remained.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/need-help-with-evm-interview-questions-gas-mapping-slot-packing
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/struggling-with-solidity-pitfalls-in-interviews-need-help
Why Communication Is a Core Skill in Blockchain QA
Blockchain QA engineers frequently act as translators between developers, security teams, and non-technical stakeholders. Communicating risk clearly — especially when uncertainty exists — is a core part of the role.
Candidates who can explain why a bug matters, what could happen if it is ignored, and how confident they are in their assessment tend to build trust quickly. This ability often outweighs raw technical depth in hiring decisions.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/web3-interview-signals-calibration
Skill Development Without Over-Engineering
Candidates often over-invest in learning every new framework or protocol, while under-investing in reasoning practice. A more effective approach is to deeply understand a smaller number of systems and practice explaining failures, trade-offs, and decisions.
Reviewing real incidents, walking through exploit write-ups, and explaining how a test could have caught an issue builds far stronger signals than expanding a tool stack endlessly.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/smart-contract-security-news-best-sources-experts-to-follow-for-real-time
These expectations become even more important when considering how the field itself is evolving and where blockchain quality engineering is headed next.
Getting Started: Your Path to Blockchain Quality Engineering
Transitioning into blockchain quality engineering is less about collecting resources and more about building correct mental models, then proving how you think.
If You’re Coming From Traditional QA
Leverage your existing strengths: test design, reproducibility, bug clarity, and risk communication already map well to blockchain work. The key shift is learning how decentralized state changes behave and how assumptions fail under adversarial conditions.
Start small: pick one ecosystem and test how transactions behave under realistic constraints. Try reproducing failures, not just “happy paths.”
If you’re balancing a full-time role while upskilling, structure matters more than motivation spikes.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/how-to-balance-full-time-work-and-blockchain-upskilling
If You’re Coming From Development
Learn testing as a discipline, not a checklist. Strong blockchain QA engineers understand what should be tested, not only how to write tests. Security-aware thinking (upgrades, access control, oracles, external calls) becomes the fastest accelerator.
Build Proof Through Small, Real Work
Instead of trying to “learn everything,” build a small track record:
explain one incident and how testing could have caught it
create a simple test plan for a contract or protocol workflow
write clearly about assumptions and failure modes
contribute test improvements to open source when possible
This aligns with how Web3 teams evaluate readiness.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/proof-based-hiring-in-web3
Where Blockchain Quality Engineering Is Headed (What’s Actually Changing)

The future of blockchain quality engineering is less about new tools and more about how responsibility is distributed as systems mature. As protocols grow in value and complexity, quality roles are moving closer to security, architecture, and decision-making rather than remaining isolated testing functions.
This shift is already visible in how teams structure hiring, interviews, and ownership. Quality engineers are increasingly expected to reason about system behavior across upgrades, integrations, and failure scenarios — not just validate individual features.
Testing Assumptions, Not Just Functionality
Modern blockchain failures rarely come from obvious bugs. They emerge when assumptions break — about oracle behavior, upgrade timing, external integrations, or economic incentives.
Quality engineers who can identify and challenge these assumptions early play a critical role in preventing downstream failures. This has pushed the role closer to design reviews and pre-deployment validation rather than post-development testing.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/silent-fails-in-smart-contract-access-control-what-teams-miss-until-its-too
Blurring Lines Between QA, Security, and Audit
The boundary between blockchain QA and security roles continues to blur. While not every quality engineer becomes an auditor, many are expected to operate with security awareness and collaborate closely with audit teams.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/smart-contract-security-audits-hub
Why Interviews Are Getting Harder (and More Subjective)
As blockchain teams mature, interviews rely less on trivia and more on judgment. Candidates are increasingly assessed on how they explain uncertainty, reason through incidents, and communicate risk.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/web3-interview-signals-calibration
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/proof-based-hiring-in-web3
Fewer QA Roles — But Higher Impact
Rather than expanding large QA teams, many blockchain companies are consolidating responsibility into smaller, senior-heavy quality or security groups. This increases the bar for entry but also increases long-term career leverage for those who adapt.
Blockchain quality engineering is no longer about keeping pace with tools or trends. It is about developing the ability to reason clearly in complex, high-risk systems. For professionals willing to build that depth, the role offers long-term relevance — even as the technology itself continues to evolve.
FAQ
1. What does a blockchain quality engineer actually do?
A blockchain quality engineer validates the safety, reliability, and behavior of blockchain systems under real conditions. This includes testing smart contracts, identifying failure scenarios, and reasoning about security and system-level risk — not just verifying expected outputs.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/smart-contract-qa-testing-hub
2. Is blockchain QA different from traditional QA or software testing?
Yes. Blockchain QA deals with immutable code, financial risk, and adversarial environments. A missed edge case can result in irreversible loss, which makes reasoning about assumptions and failure modes far more important than traditional functional testing.
why blockchain QA tests often pass locally but fail on mainnet”
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/when-blockchain-qa-tests-pass-locally-but-fail-on-mainnet-whats
3. Can I switch from traditional QA into blockchain quality engineering?
Many blockchain QA engineers come from traditional QA or test automation backgrounds. The key shift is learning how decentralized systems behave and developing security-aware thinking, rather than starting as a blockchain developer.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/moving-from-software-testing-to-blockchain-qa-need-advice
4. Do blockchain QA engineers need to know smart contract development?
Basic familiarity helps, but deep development expertise is not always required. Hiring teams care more about how candidates reason through contract behavior, upgrades, and failures than how much code they can write.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/web3-interview-signals-calibration
5. Are certifications important for blockchain QA roles?
Certifications can help with foundational learning, especially for newcomers, but they rarely decide hiring outcomes on their own. Web3 teams prioritize proof of reasoning, judgment, and real-world understanding over certificates.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/proof-based-hiring-in-web3
6. How much do blockchain quality engineers earn?
Compensation varies widely based on responsibility, security exposure, and role scope. Engineers closer to security, audits, or protocol-level decision-making tend to earn significantly more than those focused only on functional testing.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/salary-tokens-compensation-hub
7. What skills matter most for blockchain QA interviews?
Hiring teams assess how candidates think through failures, explain uncertainty, and communicate risk. Tool familiarity helps, but judgment and clarity consistently matter more.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/web3-hiring-signals
8. Is blockchain quality engineering a good long-term career?
For professionals willing to develop security awareness, system-level thinking, and strong communication, blockchain QA offers long-term relevance. As teams consolidate responsibility, fewer but more impactful roles are emerging.
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/job-search-web3-career-navigation-hub
Closing
If you’re navigating a QA-to-blockchain transition or preparing for interviews, exploring real discussions from professionals facing similar decisions often provides more clarity than generic career advice.
