Zero Knowledge Proof Explained: Privacy, zk-SNARKs, and Blockchain Applications

Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) let someone prove something is true without revealing the underlying data. In blockchain, this idea solves a fundamental tension: decentralization requires transparency, but users and applications often need privacy. ZKPs allow both to coexist, which is why they power everything from privacy chains to rollups to next-generation identity systems.
This guide starts with a beginner-friendly explanation and gradually moves into practical comparisons used by blockchain engineers and interviewers today.
What Is a Zero-Knowledge Proof?
A Zero-Knowledge Proof allows a “prover” to convince a “verifier” that a statement is correct without exposing any sensitive information.
A simple analogy:
Imagine proving you know a password without ever typing the password.
This concept underpins privacy-first systems and high-throughput blockchain designs. If you're exploring blockchain fundamentals, the community thread on how to start practicing blockchain development offers a practical beginner perspective:
How ZKPs Work
All zero-knowledge systems follow a three-step flow:
Prover creates a cryptographic proof of validity
Verifier checks the proof without accessing raw data
Blockchain updates its state using only the proof
This mechanism helps blockchains scale and stay private without relying on third-party trust.
Core Properties of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Zero-knowledge proofs satisfy three security principles:
Completeness — honest provers can always prove true statements
Soundness — false statements cannot be disguised as true
Zero-knowledge — verifiers learn nothing beyond validity
These properties are foundational in privacy-preserving smart contracts and ZK rollups. Developers preparing for interviews often reference the AOB Smart Contract Interview Prep Hub, which covers how cryptographic tools fit into practical assessments:
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/smart-contract-interview-prep-hub-peiHw2
Types of ZKPs
Interactive ZKPs
Require back-and-forth communication between prover and verifier. Used in specialized, low-latency systems.
Non-Interactive ZKPs (NIZKs)
Generate proofs in a single step. Perfect for blockchains, which cannot rely on interactive conversations.
This includes zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs — the two most important proof systems today.
⭐ zk-SNARKs vs zk-STARKs: The Clearest Practical Comparison
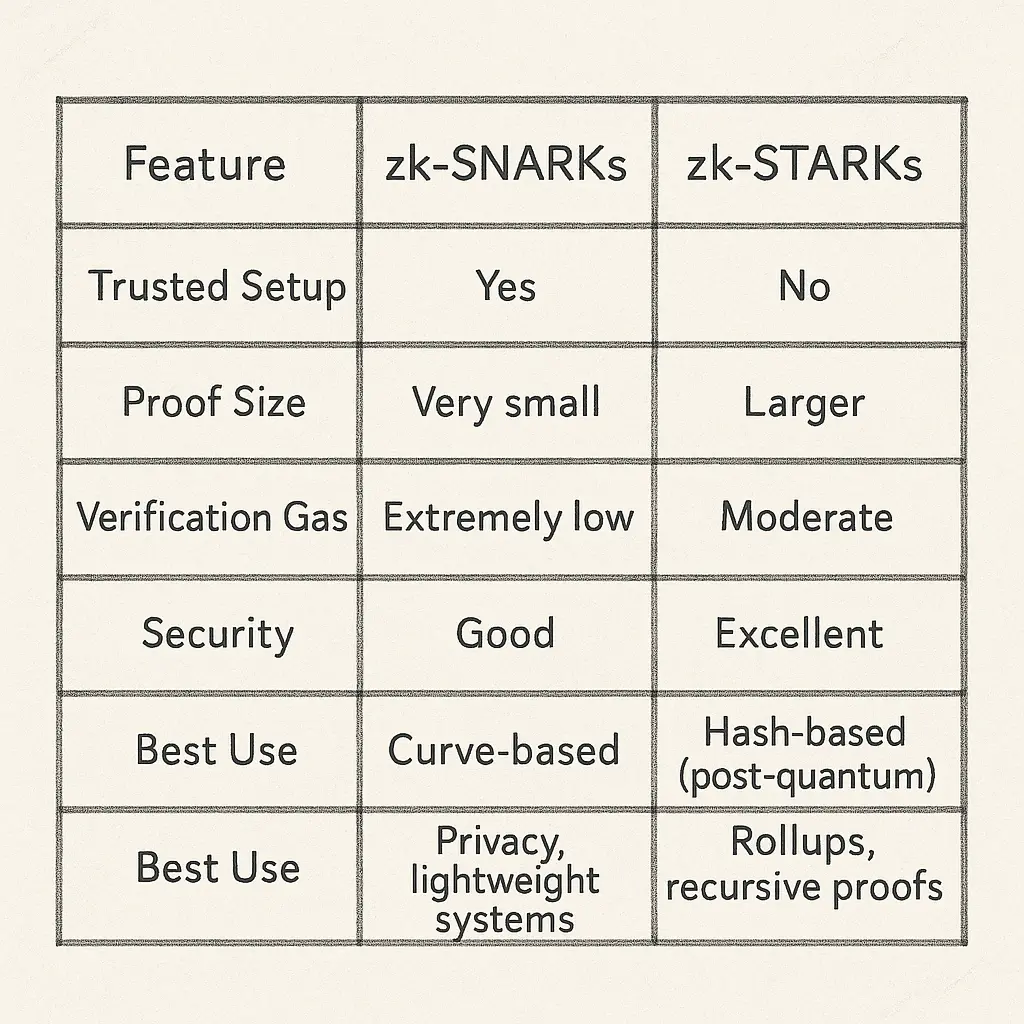
This comparison appears often in interviews and technical discussions. Below is the clean, real-world framing developers use.
What Are zk-SNARKs?
zk-SNARKs create very small proofs (around 200 bytes) that verify extremely fast on-chain.
They require a trusted setup — a one-time ceremony that generates system parameters.
Used in:
Zcash (Official docs: https://z.cash/technology/zksnarks/)
Polygon zkEVM
Early versions of Aztec
Strengths
Tiny proofs → low gas cost
Fast verification
Mature tooling
Limitations
Trusted setup introduces operational risk
Elliptic-curve based → not quantum-resistant
For candidates preparing for technical interviews, the AOB thread on gas pitfalls juniors miss pairs well with deeper ZK understanding:
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/gas-pitfalls-juniors-mention-what-interviewers-actually-assess
What Are zk-STARKs?
zk-STARKs require no trusted setup and rely on transparent, hash-based cryptography.
They scale extremely well because STARK provers parallelize heavy computations efficiently.
Used in:
StarkNet
StarkEx (Immutable X, dYdX v3)
Documentation: https://docs.starkware.co/
Strengths
No trusted setup → lower systemic risk
Hash-based → post-quantum secure
Ideal for high-volume rollups
Limitations
Larger proofs (tens to hundreds of KB)
Higher data availability cost
If you’re exploring how technical depth shapes blockchain hiring criteria, see the AOB Hiring Managers & Recruiters Hub for insights on engineering evaluation:
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/hiring-managers-recruiters-hub-hiring-signals-interview-expectations
⭐ The Most Practical SNARK vs STARK Summary
One sentence comparison:
zk-SNARKs optimize verification cost; zk-STARKs optimize scalability and long-term security.
zk-Rollups: How ZKPs Scale Blockchain
A zk-Rollup batches hundreds or thousands of transactions off-chain and submits a single validity proof to Ethereum.
How It Works
Off-chain batching
zk-SNARK/STARK proof generation
On-chain verification + compressed data posting
Rollups significantly reduce gas usage while maintaining the security of Layer-1.
For a deeper ecosystem guide, Ethereum’s official rollup documentation is a reliable reference:
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/scaling/zk-rollups/
Bulletproofs: Lightweight Privacy for UTXO-Based Systems
Bulletproofs create compact proofs (<1 kB) without a trusted setup.
They enhance confidential transactions on Bitcoin-like systems.
Original research paper: https://eprint.iacr.org/2017/1066.pdf
Where ZKPs Are Used in Practice
1. Private Transactions
Hiding transaction amounts or identities while ensuring correctness.
2. Identity & Compliance
Zero-knowledge KYC or fraud-free voting systems.
3. High-Throughput dApps
Rollups allow games, exchanges, and large contract systems to scale sustainably.
4. Cross-Chain Verification
Recursive proofs allow one chain to verify another chain’s state efficiently.
For related development challenges, see AOB’s discussion on why blockchain may be chosen over traditional databases:
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/why-choose-blockchain-instead-of-traditional-database
The Future of Zero-Knowledge: What’s Coming Next
Recursive Proofs (Plonky2, Halo2)
Enable verifying long chains of proofs cheaply
ZK + AI
Projects exploring verifiable machine learning
Enterprise Adoption
Supply chain proofs, private settlements, and auditable workflows are early use cases.
If you're exploring career alignment with these advancements, AOB’s thread on future of cybersecurity careers in Web3 provides perspective:
https://artofblockchain.club/discussion/future-of-cybersecurity-jobs-in-web3
1. What is a Zero-Knowledge Proof in simple terms?
A Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP) is a cryptographic method that lets someone prove a statement is true without revealing the underlying information. For example, you can prove you know a password without showing the password itself.
2. What is the difference between zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs?
zk-SNARKs produce very small proofs and verify fast but require a trusted setup.
zk-STARKs do not require a trusted setup, scale better, and are considered post-quantum secure, but their proofs are larger.
3. What are Zero-Knowledge Proofs used for in blockchain?
ZKPs support private transactions, identity verification without data exposure, scalable Layer-2 rollups, secure cross-chain communication, and regulatory-compliant privacy systems.
4. Are ZKPs necessary for blockchain scalability?
Yes. Zero-knowledge proofs enable zk-Rollups, which batch many transactions off-chain and submit a single proof on-chain. This reduces gas costs and increases throughput while maintaining security.
5. Why is “trusted setup” considered a risk in zk-SNARKs?
zk-SNARKs require a one-time ceremony to generate secret parameters.
If those parameters are mishandled, an attacker could generate fake proofs. This is why zk-STARKs are viewed as safer long-term.
6. Are zk-SNARKs or zk-STARKs better for smart contract developers?
It depends:
zk-SNARKs are better for low-gas, on-chain verification.
zk-STARKs are better for scaling rollups and high-volume computations.
Many teams use SNARKs today, but STARK adoption is growing.
7. Do I need advanced cryptography to learn ZKPs?
No. Most developers start with simple mental models (constraints → circuits → proofs). Modern frameworks like Circom, Noir, and Cairo allow learning ZK without deep math initially.
8. Are Zero-Knowledge Proofs used outside cryptocurrency?
Yes. ZKPs are used in identity systems, supply chain audits, private machine learning, financial compliance, and enterprise privacy solutions.
9. Are ZKPs quantum-secure?
zk-STARKs use hash-based cryptography and are considered quantum-resistant.
zk-SNARKs rely on elliptic curves, which are not quantum-secure.
10. What is a good roadmap for learning Zero-Knowledge Proofs?
Start with basics (constraints, circuits), move to SNARK/STARK comparisons, then explore tools like Circom, Cairo, and Noir. This 30-day roadmap helps beginners:
👉 https://artofblockchain.club/article/learn-zero-knowledge-proofs-zkps-in-30-days-a-beginners-roadmap
Conclusion: Why ZKPs Matter for Web3 Developers and Teams
Zero-knowledge proofs solve privacy, scalability, and security challenges that blockchains cannot address alone.
As protocols adopt rollups and privacy-preserving architectures, understanding ZKPs becomes a career advantage across engineering, auditing, and protocol design.
If you want a guided learning plan, explore our 30-day Zero-Knowledge learning roadmap:
👉 https://artofblockchain.club/article/learn-zero-knowledge-proofs-zkps-in-30-days-a-beginners-roadmap
Join the AOB community to discuss ZK developments, interviews, and skill pathways.
