Blockchain technology has been making waves in recent years, and one of its most fascinating aspects is the concept of smart contracts. But what exactly are smart contracts in blockchain, and why are they so important? In this blog, we'll break down the basics of smart contracts in blockchain technology, making it easy for beginners to understand their significance in the blockchain ecosystem.
What is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Unlike traditional contracts, which require intermediaries like lawyers or banks to enforce them, smart contracts are executed and implemented automatically by the blockchain network. The idea of smart contracts was first proposed by computer scientist Nick Szabo in the 1990s, envisioning them as a way to digitize and automate contract law. A smart contract operates like a computer program that runs when certain conditions are met, thanks to blockchain technology.
How Smart Contracts Work
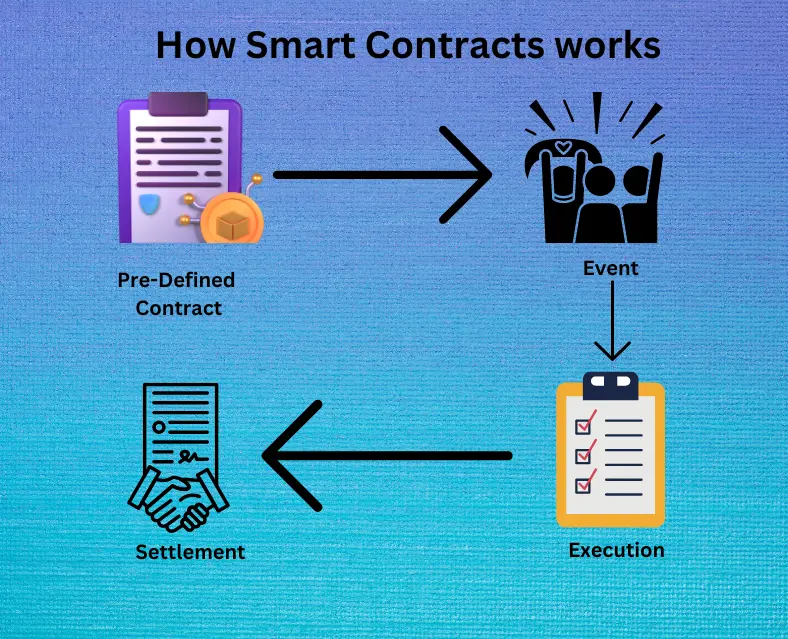
Smart contracts work by using blockchain technology to automate the execution of contractual agreements. Here's a simple breakdown of the process:
Code: The terms of the contract are written into a computer program.
Blockchain Platform: This code is deployed on a blockchain platform (e.g., Jumbo Blockchain).
Participants: Parties involved in the contract interact with it through the blockchain.
Once the conditions specified in the contract are met, the smart contract automatically executes the agreed-upon actions. For example, if a smart contract is set to release a payment when goods are delivered, it will automatically transfer the funds when the delivery is confirmed on the blockchain.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts in blockchain technology offer several advantages over traditional contracts:
Automation and Efficiency: It eliminates the need for intermediaries, speeds up the process, and reduces the chances of human error.
Transparency and Trust: The process can be trusted by all parties because the contract's terms are visible and verifiable on the blockchain.
Security and Immutability: Once a smart contract is deployed, it cannot be altered, ensuring that the terms remain the same.
Cost Savings: By cutting out intermediaries, smart contracts can significantly reduce transaction costs.
Use Cases of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have a wide range of applications across various industries:
Financial Services: They can automate payments, insurance claims, and more, ensuring faster and more accurate transactions.
Supply Chain Management: Smart contracts can track the movement of goods, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud.
Real Estate Transactions: They can streamline the buying and selling process, reducing paperwork and speeding up transactions.
Healthcare: Smart contracts can manage patient data securely, ensuring only authorized personnel have access.
Digital Identity and Voting Systems: They can create secure, tamper-proof systems for identity verification and voting, ensuring integrity and transparency.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite their many benefits, smart contracts in blockchain technology also face several challenges:
Technical Complexity: Creating and deploying smart contracts requires specialized knowledge and skills.
Legal and Regulatory Issues: The legal status of smart contracts is still evolving, and they may not be recognized in all jurisdictions.
Security Vulnerabilities: Bugs or vulnerabilities in the code can lead to significant losses or exploitation.
Scalability Concerns: Blockchain networks can become congested, slowing down the execution of smart contracts.
Future of Smart Contracts
The future of smart contracts in blockchain technology looks promising, with ongoing developments aimed at overcoming current limitations. Potential advancements include:
Integration with Emerging Technologies: Combining smart contracts with technologies like IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) can create even more robust applications.
Increasing Adoption: As more industries recognize their benefits, the use of smart contracts is expected to grow, driving further innovation.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are revolutionizing the way we think about agreements and transactions. They offer immense potential to transform various industries by automating and securing contractual processes. As you explore the world of blockchain technology, understanding smart contracts will give you valuable insight into its transformative power. Keep learning and stay curious about this exciting technological frontier!

